DRIVE CONNECTIONS | USB | USB-C | THUNDERBOLT | SD CARDS | DOCSIS |
See the Best TVs of 2025 From CNET
(Plasma) In the early days of flat-panel High Definition TVs, plasma, with its inky blacks and top-notch picture quality, was the prevalent flat-panel technology, especially among videophiles. Now, Plasma has been overtaken and supplanted by LCD/LED technology.
See this How-to-Geek article to find out what happened to Plasma TVs.
Not sure what LED is? This How-to-Geek article explains.
(LCD) Liquid Crystal Display, (LED) Light-Emitting Diode technology replaced Plasma screens even though picture quality was and is subpar to Plasma. LCDs with LED backlighting, became less expensive and more capable, and finally overtook plasma in popularity.
(QLED) or quantum dot LED TV is a LED screen technology that adds a quantum dot film to the LCD. Unlike OLED the quantum dots are transmissive rather than emissive and rely on an LED backlight. Seen primarily in Samsung and TCL branded TVs.
(OLED) An organic light-emitting diode is a light-emitting diode (LED) screen technology in which the emissive electroluminescent layer is a film of organic compound that emits light in response to an electric current. OLED began and is still more expensive than LCD/LEDs, but OLED now produces picture quality generally as good or better than Plasma, mostly seen in high-end TVs and smartphones. All OLED display panels are manufactured by either LG or Samsung.
(AMOLED) active-matrix organic light-emitting diode, screen technology as seen on the brightest high-end smart phones and tablets, a step forward from OLED for small display screens.
The next advance in LED displays will be called Mini-LED and Micro-LED.
Mini-LEDs will likely be used in normal-sized screens such as PC and tablet screens and regular sized TVs (up to 65" or even 75"). For more detailed information on Mini-LED TVs and displays see OLED vs. Mini-LED: The PC displays of the future, compared from PC World Magazine.
Micro-LEDs are modular in nature and will probably be used primarily in extra large screens such as Sony's Crystal LED and Samsung's The Wall, which use millions of LEDs, one for each pixel. Micro-LEDs are currently much more expensive than other LED technologies, including Mini-LEDs.
(for TVs and PC displays)
Image resolution formats define how many pixels (individual picture elements) are present on a video screen.
(HD) High Definition 720p image resolution (1,280 x 720 or 921,600 pixels), sometimes (1366 x 768 pixels)
(FHD) Full High Definition 1080p image resolution (1920 x 1080 or 2,073,600 pixels)
(QHD) 1440p or Quad High Definition is a display resolution that measures 2560 x 1440 or 3,686,400 pixels. This resolution is also commonly referred to as 2K. Also sometimes called WQHD or Wide Quad High Definition.
(UHD) Ultra High Definition 4K image resolution (3840 x 2160 or 8,294,400 pixels)
8K or sometimes (8K UHD) image resolution (7,680 x 4,320 or 33,177,600 pixels) 8K TVs are starting to hit the market, but it's going to be a while (years) before this resolution is common or these displays are reasonably affordable.
"Resolution is one of the most common specifications used to sell TVs, partly because "4K" and "8K" sound really high-tech and impressive. However, resolution is not the most important ingredient in picture quality. Just because a TV has higher resolution than another, doesn't always mean it's looks better. It might, but not always, and for reasons that have little to do with resolution. A TV with better high dynamic range (HDR) performance, a better overall contrast ratio or better color will look better than one that just has more pixels." (CNET)
High-dynamic range (HDR) TV, when showing HDR content, has a wider dynamic range (contrast ratio), along with more steps in brightness (for smother transitions and more detail in bright and shadowy areas). Also, usually, HDR is paired with Wide Color Gamut (WCG), which offers a greater range and depth of color.
However, to take advantage of HDR's benefits you must be viewing special HDR content.
Finally, HDR for TV is not the same as HDR for photography
For a more detailed explanation of HDR for television see this CNET article.
BTW, if you are planning to buy a new TV specifically for gaming, How-to-Geek has a great article called How to Buy a TV for Gaming in 2020. This article decodes and explains all the new acronyms specific to the needs of super high definition gaming.
Or see this updated article from PC Magazine The Best TVs for Gaming

(VGA) Video Graphics Array with analog signal, does not carry audio

(DVI) Digital Visual Interface signal, normally same as HDMI, but without audio. Mostly on PCs but now being supplanted by HDMI

(HDMI) High Definition Multimedia Interface with digital signal, can also carry audio, seen on both PCs and TVs. Version 2.0 added support for 4K video and Version 2.1 added support for high-bandwith 8K video. All connectors and cables must be rated the same for higher resolutions.
See: Does it matter which HDMI port you use on your TV? Short answer: Yes from ZDNET

(DisplayPort) Primarily a computer connection format for 4K 3840 x 2160-pixel resolution at 60fps, can also carry audio. Displayport 2.0 promises 8K video support by late 2020.
HDMI vs. DisplayPort: Which Should I Use for My PC Monitor? from PC Magazine

There is also a (MiniDP) or mDP Mini DisplayPort, which is a miniaturized version of the DisplayPort audio-visual digital interface, used mostly as a computer connection format (very little on televisions). Note: MiniDP ports on high-end PCs have now been supplanted by USB-C and/or Thunderbolt ports.
SATA - Serial Advanced Technology Attachment is an IDE standard first released in 2001 for connecting devices like optical drives and hard drives to the motherboard. The term SATA generally refers to the types of cables and connections that follow this standard.
An IDE Integrated Drive Electronics hard drive is commonly referred to as an ATA or PATA (parallel ATA) hard drive, Which is conneted to the PC motherboard by a 40 pin connector plus a 4 pin power connector.
The more modern SATA, Serial ATA devices consist of an 8 mm wide wafer connector on each end and the cable has a 7-pin connector.
The SATA Serial connection eliminates the old master/slave PATA cofiguration to determine the boot drive and is also much faster, up to 600 MB/s compared to PATA's 133 MB/s top speed.

Shown at half size, a modern 3.5" 7200 RPM SATA hard disk drive

Shown, modern 2.5" SSD drive
Even more modern (more durable and faster) SSDs or Solid State Drives can be connected using SATA connectors or M2 SATA slots on the motherboard.

Shown, the latest PCIe NVME SSD drive
A newer and much faster connection for SSDs is called M2 NVMe non-volatile memory express, which is connected to the high-speed Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe), commonly called PCI Express. This is a very fast connection, up to 4 times the speed of a regular SATA connetion.
The latest PCIe NVMe SSDs can read and write data to the drive 4 times faster than regular SATA drive but they can also locate data (Seek Time) on a drive 10 times as fast as other drives.
All of this speed means, that if the operating systems and program files are located on the SSDs these PCs will be much faster and more durable than anthing else that has come before. These speeds are not quite fast enough for instant-on Windows PCs, but we're getting there. See my SSD page for more information about these speedy new drives.
Universal Serial Bus
USB ports and versions:
connection used to connect Computers (PCs) to:
- Printers
- Scanners
- Mice
- Joysticks
- Flight yokes
- Digital cameras
- Webcams
- Modems
- Speakers
- Telephones
- Video phones
- Storage devices
- Medical devices
- Network connections
USB versions Note: Later version features sometimes overlap
USB 1.1 created in 1998 can transfer data at up to 12Mbps (Megabits per second).
USB 2.0 created in 2000 can transfer data at up to 480 Mbps.
USB 3.0 created in 2008 can transfer data at up to 5 Gbps (Gigabits per second). Note: Now also called USB version 3.1 Gen 1 or 3.2 Gen 1 or simply SuperSpeed USB.
USB 3.1 created in 2015 can transfer data at up to 10Gbps. Note: Now also called USB 3.1 Gen 2 or USB 3.2 Gen 2 and SuperSpeed USB 10 Gbps.
USB 3.2 created in 2016 can transfer data at up to 20 Gbps. Note: Now also called USB version 3.2 Gen 2X2 or SuperSpeed USB 20Gbps
Note: In order to achieve the highest rated speeds and data rates all connected devices must be of the same version.
USB Version 3.0, 3.1, and 3.2 are sometimes marked with blue tabs inside the female and male ports and plugs or with SS (for Super Speed USB)
If the current version labeling scheme continues it is possible the upcoming USB version 4.0 may be just as jumbled and confusing.
Update 10/03/2022
Thankfully the USB Implementers Forum (USB-IF) has now come up with a much better labeling scheme.
Here's an example:

USB Types and connectors
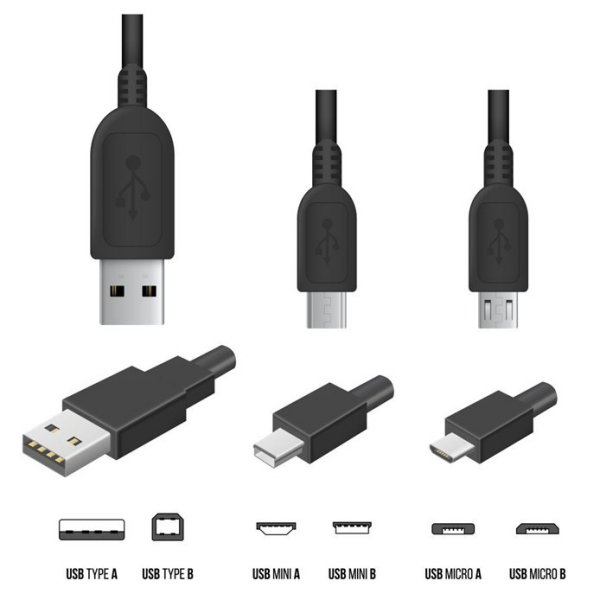

USB type A and B connectors
NOT reversible or interchangeable except through the use of dongles or adaptors.

USB-C, created in 2016, is roughly one third the size of the common USB-A port and connector. It has a 24-pin reversible plug and its small size makes its ports ideal for use on the new thin PC's, tablets and Smartphones.
The new USB Type-C Specification Revision 2.1 now supports power delivery up to 240 watts (was 100 watts) and Video as well as data transfer for connections of either USB Version 3.1 Gen 1 at 5 Gbps and USB Version 3.1 Gen 2 at 10 Gbps or sometimes USB Version 3.2 at up to 20 Gbps. The latest USB version to be introduced is Version 4, which promises data transfer rates at up to 40 Gbps, on par with Thunderbolt 4. (see below)
Note: To achieve these rated speeds all connectors and cables used must rated the same version.
USB-C is backwards compatible with earlier USB versions and can be interconnected with other types of USB cables and ports with commonly available dongles and docking stations.
Throughput speeds will always be that of the lowest version devices connected.
If you wish more detailed information on USB-C check out this excellent article from PC Magazine.
Also: How to Geek has a helpful article which helps you decide which file system you should use on your USB drive.

Including USB4
Even though Thunderbold is not an acronym its inclusion here is a natural progression since Thunderbolt uses the USB-C port to increase throughput.
The earliest version of Thunderbolt, created in 2011, used miniDisplayPort connectors and could transfer data at up to 10 Gbps when Apple was the primary user. Thunderbolt version 2 from 2013 could transfer data at 20 Gbps.
Now the latest Thunderbolt 3 version (late 2015, early 2016) uses the USB Type C connector and port to achieve connection speeds of up to 40 Gbps (Gigabits per second, power delivery up to 100 watts and multiple 4K video connections).
Even though Thunderbolt is a proprietary Intel protocol and has been reserved for devices which use Intel processors, full support for PCs with AMD processors is in the works and upcoming.

Thunderbolt connectors and ports are marked with a lightning bolt and are commonly found on high-end laptop PC's from manufacturers such as Apple, Dell, and Hewlett Packard (HP).
Note: Even though Thunderbolt is backward compatible with USB-C right now any USB Type-C device or cable plugged into a Thunderbolt 3 port won't support Thunderbolt full features and speed. Also Thunderbolt 3 peripherals plugged into a regular USB Type-C port won't support Thunderbolt features either.
However the upcoming USB version 4 protocol is slated to support Thunderbolt 3 devices and capabilities.
Update: 09/03/2022 - USB4 leaps ahead of Thunderbolt with 80Gbps standard from PC World Magazine and 10/23/2022 Next-generation of Intel Thunderbolt will also hit 80Gbps also from PC World Magazine
If you work from home:
Best Thunderbolt Docks for Laptops From PC World Magazine


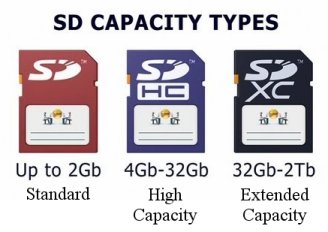
Note: As of this writing, the largest capacity SDXC card you can purchase is 1TB, which was introduced in September of 2016 by SanDisk.
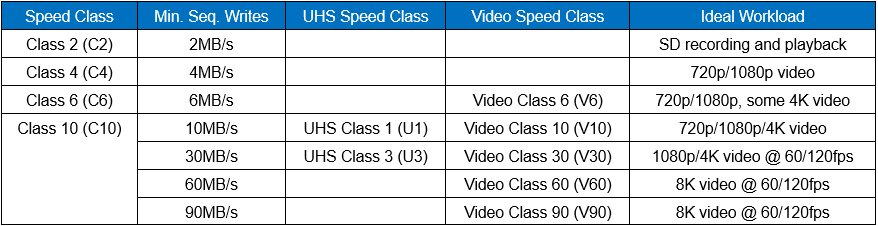
In addition to the Standard Speed classes SD cards are also available in two faster speed classes. The first is called Ultra High Speed or UHS.
The first is UHS class 1 speed which is 10 Megabytes per second or 10MB/s.
The second is UHS class 2 speed, which is 30 Megabytes per second or 30MB/s.
The newest speed class is called Video Speed Class.
The Video Speed Class is as follows: V10 is 10MB/s, V30 is 30MB/s, V60 is 60MB/s and V90 is 90MB/s.
The table below shows the speed classes and workloads. Keep in mind that the higher capacity and faster SD cards will carry a hefty price increase.
A1 vs A2?
In addition to all the other SD card ratings we also have what is called the Application Performance Class. According to the SDcard.org "The Application Performance Class was introduced to realize comfortable application manipulation such as compilation of data which is stored in an SD memory card." Therefore, most experts recommend a SD card with an A2 rating (Application Speed Class 2) since "It makes SD memory card much higher performance than A1 performance by using functions of Command Queuing and Cache."
Example Amazon listing - SanDisk Extreme Pro Micro SDXC UHS-I U3 A2 V30 Memory Card
 If you need some help choosing a new SD card see The best microSD cards you can buy from ZDNet
If you need some help choosing a new SD card see The best microSD cards you can buy from ZDNet
DOCSIS version 3.1 is now the latest standard, but the recently approved DOCSIS 4.0 is expected to provide an even better streaming experience as well as faster upload speeds once the new devices finally start rolling out to consumers.

Since most WIFI systems depend on Cable Modem speed and reliability this is important. Read this article from Tom's Guide that explains all about DOCSIS 4.0.